Abstract

Introduction: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has shown durable responses in 40-50% of patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL). For patients who progress after CAR-T, there is no standard salvage strategy and data is limited. Clinical trials are favored in this context but not all patients have access in their centers nor meet inclusion criteria. More information on treatment outcomes in this setting is warranted to inform decision-making in this rising patient population.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, multicenter study including all patients with R/R LBCL infused at 12 sites with commercially available CAR T-cell products until June 2022 who had a confirmed progression on imaging and/or biopsy and at least 1 month of follow-up. We analyzed the baseline characteristics, response rates across main types of treatment and survival outcomes. The univariate and multivariate logistic regression was carried out to study the association between different variables with the possibility of receiving treatment after CAR-T progression. Survival analysis, including progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was carried out with the Kaplan-Meier method and the univariate Cox analysis was used for statistical comparison.
Results: The study included 217 patients, 79 (36%) received palliative care (NT group) and 138 (64%) patients received treatment (T group). In the latter, we identified 4 main subgroups as first-line salvage: Rituximab-Polatuzumab-Bendamustine (POLA, N=31), bispecific antibodies (BITE, N=27) in monotherapy or combination, standard chemotherapy (CT, N=27) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI, N=23). Other strategies included radiotherapy (N=17) and lenalidomide-based regimens (N=4).
Median follow-up since relapse/progression for the full cohort was 17 months (CI95% 13-22 months). Regarding baseline characteristics (Table 1), age, pretreatment IPI score, ECOG, achieving an initial response after CAR-T and time from infusion to progression showed a significant impact on the possibility of receiving treatment after CAR-T progression in the univariate analysis. In the multivariate analysis, age, as a continuous variable, retained the significant impact (p=0.003).
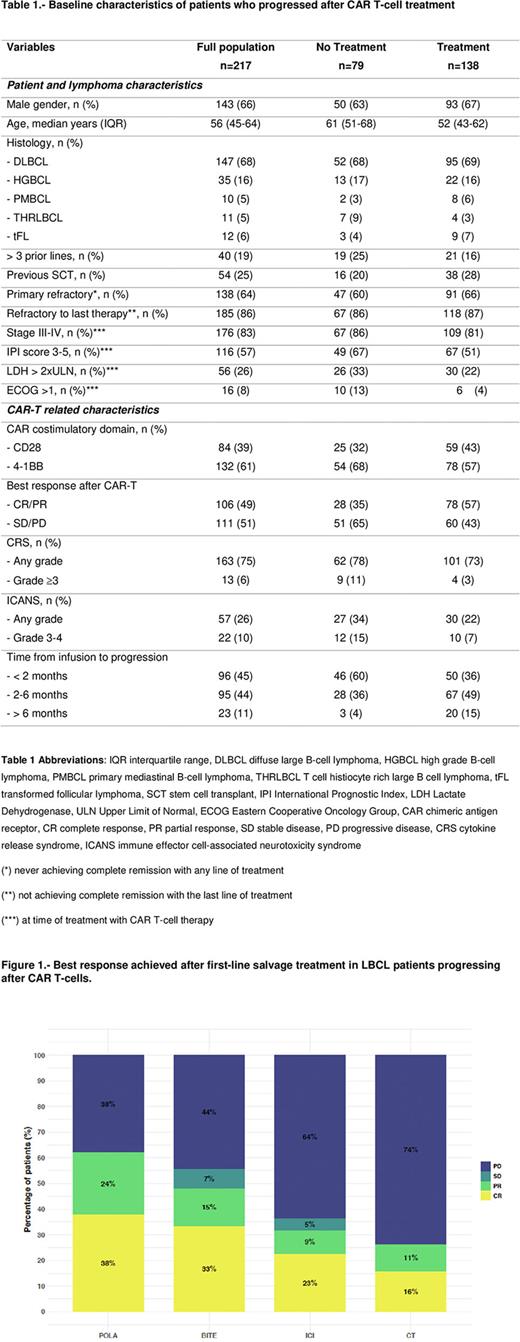
Best response after first line salvage treatment included an overall (complete, CR) response rate of 62% (38%) for POLA, 48% (33%) for BITE, 32% (23%) for ICI and 27% (16%) for CT. Regarding the ICI group, CAR-T flow data was available in 12 (52%) patients before and after the start of this salvage regimen. Two (17%) patients had a confirmed re-expansion after receiving the first dose of ICI, both in ongoing remission without a transplant consolidation.
Median PFS for the full T cohort was 3.1 months and 12-month PFS was 18%. Median PFS for the POLA, BITE, ICI and CT groups was 6.1, 4.7, 2.7, and 2.1 months, respectively. Considering CT as the reference group, only POLA showed a significant PFS improvement (p=0.02). Median OS for the full cohort was 5 months, significantly longer in the T vs NT groups (7.6 vs 1.1 months, respectively, p <0.01). The 12-month OS for the NT and T groups was 7% vs 35%, respectively. Time from CAR-T infusion to disease progression, divided in 3 groups (<2 months, 2-6 months and >6 months) showed significant OS differences (3.0 vs 5.9 vs NR, respectively, p <0.01). Regarding the main subgroups of the T cohort, there were no significant OS differences.
Fifteen (11%) patients of the T group received an allogeneic stem cell transplant (allo-SCT) as consolidation after responding to salvage treatment with CT (N=7, 26%), POLA (N=4, 13%), radiotherapy (N=3, 18%) or BITE (N=1, 4%). With a median follow-up after transplant of 11.1 months (range 1.0-28.6 months), 3 patients had progressed (2 CT group, 1 POLA group) and 4 had died (including the 3 patients in progression and 1 due to CMV encephalitis). Median OS was not reached.
Conclusions: Patients with LBCL progressing early after CAR T-cell therapy have poor survival outcomes. Salvage strategies with polatuzumab-containing regimens and bispecific antibody-based trials yield higher response rates in comparison to standard chemotherapy. Consolidation with an allo-SCT after achieving a response in this setting should be discussed in all potential candidates.
Disclosures
Iacoboni:NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE: Consultancy; NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE, ASTRAZENECA, ROCHE, ABBVIE, JANSSEN, MILTENYI: Honoraria. Mussetti:GILEAD: Research Funding; TAKEDA: Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy; JAZZ PHARMACEUTICALS: Consultancy. Caballero Gonzalez:Novartis, Gilead: Honoraria. Sancho:Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria; Sandoz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kern Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi Biomedicine: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria; BeiGene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celltrion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eli Lilly & Company: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Barba:BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Kwon:BMS: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel. Sureda:NOVARTIS: Consultancy, Honoraria; SANOFI: Consultancy, Honoraria; ROCHE: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; JANSSEN: Consultancy, Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; TAKEDA: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; GILEAD: Consultancy. Martín García-Sancho:Miltenyi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Incyte: Consultancy, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Kern: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Clinigen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Lilly: Consultancy, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; ADC Therapeutics America: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel. Abrisqueta:Sandoz: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Checkpoint inhibitors are not approved for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma but are used in the context of progression after CAR T-cell therapy. Bispecific antibodies are used in the setting of clinical trials.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal